AWS CLI: 7 Powerful Ways to Master Cloud Control Instantly
Want to control your AWS cloud like a pro without clicking through endless menus? The AWS CLI is your ultimate shortcut—fast, powerful, and built for efficiency. Let’s dive into how you can harness its full potential.
What Is AWS CLI and Why It’s a Game-Changer

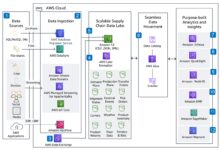
The AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) is a unified tool that allows developers and system administrators to interact with Amazon Web Services through commands in a terminal or script. Instead of navigating the AWS Management Console with a mouse, you can automate tasks, manage resources, and scale infrastructure using simple text-based commands.
Understanding the Core Functionality
The AWS CLI acts as a bridge between your local machine and AWS services. It supports over 200 AWS services, including EC2, S3, Lambda, IAM, and RDS. Whether you’re launching an EC2 instance or uploading files to S3, the CLI streamlines the process into a few concise commands.
- Direct access to AWS APIs via command-line syntax
- Support for JSON input and output for structured data handling
- Integration with shell scripts and automation tools
Key Advantages Over the Web Console
While the AWS Management Console offers a user-friendly graphical interface, the AWS CLI provides precision, speed, and repeatability. For example, launching 10 EC2 instances manually takes time and is error-prone. With the CLI, you can write a single command or script to do it instantly and consistently.
- Automation: Run repetitive tasks without manual intervention
- Faster execution: Commands execute in seconds, not clicks
- Version control: Scripts can be stored in Git for audit and collaboration
“The AWS CLI turns infrastructure into code—making it repeatable, testable, and scalable.” — AWS Official Documentation
How to Install and Configure AWS CLI
Getting started with the AWS CLI involves two main steps: installation and configuration. Once set up, you’ll have direct access to your AWS environment from any terminal window.
Installation on Different Operating Systems
The AWS CLI can be installed on Windows, macOS, and Linux. The installation method varies slightly depending on your OS.
- macOS: Use Homebrew with
brew install awscli - Linux: Use pip (Python package manager) via
pip install awscli - Windows: Download the MSI installer from the official AWS CLI page or use pip
For advanced users, AWS also provides the AWS CLI v2, which includes built-in support for assuming roles, improved auto-suggestions, and better error messages.
Configuring AWS CLI with Credentials
After installation, run aws configure to set up your credentials. You’ll need:
- AWS Access Key ID
- AWS Secret Access Key
- Default region name (e.g., us-east-1)
- Default output format (json, text, or table)
These credentials are stored in ~/.aws/credentials and should be protected. Never commit them to version control. For enhanced security, use IAM roles when running on EC2 instances or leverage AWS Single Sign-On (SSO) for enterprise environments.
Mastering Basic AWS CLI Commands
Once configured, you can start using the AWS CLI to manage your cloud resources. Here are some foundational commands every user should know.
Navigating S3 with AWS CLI
Amazon S3 is one of the most commonly used services with the AWS CLI. You can upload, download, and manage buckets and objects efficiently.
- Create a bucket:
aws s3 mb s3://my-unique-bucket-name - Upload a file:
aws s3 cp local-file.txt s3://my-bucket/ - Sync folders:
aws s3 sync ./local-folder s3://my-bucket/backup - List bucket contents:
aws s3 ls s3://my-bucket
The sync command is especially powerful—it only transfers changed files, making it ideal for backups and deployments.
Managing EC2 Instances via CLI
EC2 instances can be launched, monitored, and terminated using the AWS CLI. This is crucial for DevOps teams automating infrastructure.
- Launch an instance:
aws ec2 run-instances --image-id ami-0abcdef1234567890 --instance-type t2.micro --key-name MyKeyPair --security-group-ids sg-903004f8 --subnet-id subnet-6e7f829e - List running instances:
aws ec2 describe-instances --filters "Name=instance-state-name,Values=running" - Stop an instance:
aws ec2 stop-instances --instance-ids i-1234567890abcdef0 - Terminate an instance:
aws ec2 terminate-instances --instance-ids i-1234567890abcdef0
You can filter results using JMESPath queries to extract specific fields, such as public IP addresses or instance types.
Advanced AWS CLI Features You Should Know
Beyond basic commands, the AWS CLI offers advanced capabilities that boost productivity and enable complex automation workflows.
Using JMESPath for Output Filtering
JMESPath is a query language for JSON that allows you to filter and format AWS CLI output. Instead of parsing raw JSON manually, you can extract exactly what you need.
- Get only instance IDs:
aws ec2 describe-instances --query 'Reservations[*].Instances[*].InstanceId' --output json - Filter by state:
aws ec2 describe-instances --query 'Reservations[*].Instances[?State.Name==`running`].InstanceId' - Format as table:
aws ec2 describe-instances --query 'Reservations[*].Instances[*].[InstanceId, InstanceType, State.Name]' --output table
This feature is indispensable when scripting or generating reports from CLI output.
Working with Pagination and Large Result Sets
Some AWS API calls return large datasets that are paginated. By default, the AWS CLI retrieves only the first page. To get all results, use the --page-size and --max-items options or enable --no-paginate.
- Fetch up to 1000 S3 objects:
aws s3api list-objects-v2 --bucket my-bucket --max-items 1000 - Use pagination:
aws ec2 describe-regions --paginate - Combine with JMESPath to extract values across pages
Understanding pagination ensures your scripts don’t miss data when querying services like CloudTrail or Config.
Automating Tasks with AWS CLI Scripts
One of the biggest strengths of the AWS CLI is its ability to be integrated into scripts for automation. This is essential for CI/CD pipelines, scheduled backups, and infrastructure provisioning.
Writing Bash Scripts with AWS CLI
You can combine AWS CLI commands with shell scripting to create powerful automation tools. For example, a script that backs up logs daily:
#!/bin/bash
TIMESTAMP=$(date +%Y%m%d-%H%M%S)
aws s3 cp /var/log/app.log s3://my-logs-backup/app-log-$TIMESTAMP.txt
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Backup successful"
else
echo "Backup failed"
fiSuch scripts can be scheduled using cron jobs on Linux or Task Scheduler on Windows.
Integrating with CI/CD Pipelines
In DevOps environments, the AWS CLI is often used in tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI to deploy applications. For example:
- Deploy a Lambda function:
aws lambda update-function-code --function-name my-function --zip-file fileb://function.zip - Update an ECS service:
aws ecs update-service --cluster my-cluster --service my-service --force-new-deployment - Push Docker images to ECR:
aws ecr get-login-password | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin <account-id>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com
By embedding AWS CLI commands in pipeline scripts, teams achieve consistent, repeatable deployments.
Solving Common AWS CLI Errors and Issues
Even experienced users encounter errors when working with the AWS CLI. Knowing how to troubleshoot them saves time and prevents frustration.
Authentication and Permission Errors
One of the most common issues is InvalidClientTokenId or AccessDenied errors. These usually stem from incorrect or expired credentials.
- Verify credentials with
aws sts get-caller-identity - Check if the IAM user or role has the required permissions
- Ensure MFA is not required without proper session token setup
If using temporary credentials (e.g., from STS), make sure the session hasn’t expired.
Region and Endpoint Mismatch Problems
Some services are region-specific. If you get a NotFound or Unknown endpoint error, double-check your region settings.
- Set default region in config:
aws configure set default.region us-west-2 - Specify region per command:
aws s3 ls --region eu-central-1 - Use
aws ec2 describe-regionsto list available regions
Also, ensure the service you’re accessing is available in the selected region.
Best Practices for Secure and Efficient AWS CLI Usage
To get the most out of the AWS CLI while maintaining security and reliability, follow these industry-recommended practices.
Secure Credential Management
Never hardcode AWS credentials in scripts. Instead, use one of these secure methods:
- IAM Roles for EC2 instances (no keys needed)
- AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store for secrets
- Environment variables (with caution)
- AWS SSO for federated users
Rotate access keys regularly and use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for root and privileged accounts.
Optimizing Performance and Reliability
To ensure your CLI operations are fast and resilient:
- Use
--output textor--queryto minimize data transfer - Enable retries with exponential backoff for transient failures
- Use
aws configure set cli_auto_prompt onfor interactive mode (CLI v2) - Cache credentials and assume roles efficiently
Also, monitor API usage with AWS CloudTrail to detect anomalies or excessive calls.
Real-World Use Cases of AWS CLI in DevOps
The AWS CLI isn’t just a tool for individual commands—it’s a cornerstone of modern DevOps practices. Let’s explore how teams use it in production environments.
Infrastructure as Code with AWS CLI and CloudFormation
While tools like Terraform and AWS CloudFormation are declarative, the AWS CLI can trigger and manage stacks programmatically.
- Create a stack:
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name my-app --template-body file://template.yaml --parameters ParameterKey=InstanceType,ParameterValue=t3.micro - Update a stack:
aws cloudformation update-stack --stack-name my-app --template-body file://updated-template.yaml - Monitor stack events:
aws cloudformation describe-stack-events --stack-name my-app
This integration allows developers to automate environment provisioning in CI/CD pipelines.
Automated Backups and Disaster Recovery
Many organizations use the AWS CLI to automate EBS snapshots, RDS backups, and S3 versioning.
- Create EBS snapshot:
aws ec2 create-snapshot --volume-id vol-1234567890abcdef0 --description "Nightly backup" - Copy RDS snapshot across regions:
aws rds copy-db-snapshot --source-db-snapshot-identifier my-snapshot --target-db-snapshot-identifier my-snapshot-copy --source-region us-east-1 --target-region eu-west-1 - Delete old snapshots:
aws ec2 describe-snapshots --owner self --query 'Snapshots[?StartTime<`2023-01-01`].[SnapshotId]' --output text | xargs -I {} aws ec2 delete-snapshot --snapshot-id {}
These scripts ensure data resilience and compliance with retention policies.
Future of AWS CLI: Trends and Upgrades
As cloud environments grow more complex, the AWS CLI continues to evolve. Staying updated with new features ensures you remain efficient and secure.
AWS CLI v2 Enhancements
AWS CLI version 2 introduced several quality-of-life improvements:
- Interactive mode with auto-suggestions
- Built-in support for assuming IAM roles
- Improved installation experience (no Python dependency on some platforms)
- Stable support for AWS SSO
It’s recommended to upgrade from v1 to v2 for better performance and security.
Integration with AWS SDKs and Tools
The AWS CLI is built on top of the AWS SDK for Python (Boto3). As new services launch, the CLI is updated to support them quickly. Future integrations may include tighter coupling with AWS CDK, enhanced AI-driven suggestions, and better cross-service automation.
- Support for AWS Copilot and ECS CLI
- Deeper integration with AWS AppConfig and Systems Manager
- Improved error diagnostics and contextual help
Keeping your CLI updated ensures access to the latest capabilities.
What is AWS CLI used for?
The AWS CLI is used to manage Amazon Web Services from the command line. It allows users to control EC2 instances, S3 buckets, Lambda functions, and other AWS resources using text commands, enabling automation, scripting, and efficient cloud management.
How do I install AWS CLI on Windows?
You can install AWS CLI on Windows by downloading the MSI installer from https://aws.amazon.com/cli/ or using pip: pip install awscli. After installation, run aws configure to set up your credentials.
How can I fix AWS CLI ‘Access Denied’ errors?
Check your IAM permissions, ensure your credentials are valid and not expired, and verify that MFA isn’t required without a session token. Use aws sts get-caller-identity to confirm your identity and permissions.
Can I use AWS CLI with IAM roles?
Yes, you can use AWS CLI with IAM roles. When running on EC2, assign an IAM role to the instance. For local use, configure role assumption in ~/.aws/config using role_arn and source_profile.
Is AWS CLI free to use?
Yes, the AWS CLI itself is free. You only pay for the AWS services you use through it, such as EC2 instances, S3 storage, or Lambda invocations.
The AWS CLI is more than just a command-line tool—it’s a gateway to efficient, scalable, and automated cloud management. From installing and configuring to scripting and troubleshooting, mastering the AWS CLI empowers developers, DevOps engineers, and administrators to work faster and smarter. Whether you’re managing a single S3 bucket or orchestrating a global infrastructure, the CLI gives you the control and flexibility you need. As AWS continues to innovate, staying proficient with the CLI ensures you’re always ready to leverage the latest cloud capabilities.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: