AWS 101: 7 Powerful Reasons to Master Amazon Web Services Now
Welcome to the ultimate guide on Amazon Web Services (AWS), the powerhouse behind modern cloud computing. Whether you’re a developer, entrepreneur, or IT pro, understanding AWS is no longer optional—it’s essential.
What Is AWS and Why It Dominates the Cloud

Amazon Web Services, commonly known as AWS, is the world’s most comprehensive and widely adopted cloud platform. Launched in 2006, AWS offers over 200 fully featured services from data centers globally, serving millions of customers—including startups, enterprises, and government agencies.
The Birth of AWS: A Game-Changer in Tech
AWS wasn’t just another product launch—it revolutionized how businesses think about infrastructure. Before AWS, companies had to invest heavily in physical servers, data centers, and maintenance. AWS introduced a pay-as-you-go model, allowing organizations to scale resources up or down based on demand.
- AWS began as an internal project to streamline Amazon’s own infrastructure.
- It launched publicly with Simple Storage Service (S3) and Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2).
- Today, AWS powers 40% of all cloud workloads worldwide.
“AWS didn’t just enter the market—it created the market for cloud computing as we know it.” — TechCrunch
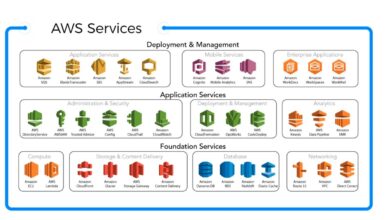
Core Components That Define AWS
AWS isn’t a single service but a vast ecosystem. Its architecture is built around compute, storage, networking, and management tools that work seamlessly together.
- Compute: Services like EC2, Lambda, and ECS allow flexible processing power.
- Storage: S3, EBS, and Glacier provide scalable, durable, and cost-effective storage.
- Networking: VPC, Route 53, and CloudFront enable secure and fast global connectivity.
These components are the backbone of AWS, making it adaptable for everything from small apps to enterprise-grade systems.
7 Key Benefits of Using AWS
Why has AWS become the go-to choice for so many organizations? The answer lies in its unmatched advantages that drive innovation, reduce costs, and accelerate time-to-market.
1. Unparalleled Scalability and Flexibility
One of the most powerful features of AWS is its ability to scale on demand. Whether you’re launching a new app or handling seasonal traffic spikes, AWS adjusts automatically.
- Auto Scaling groups ensure your applications maintain performance during peak loads.
- Serverless options like AWS Lambda eliminate the need to manage servers entirely.
- You can deploy resources across multiple Availability Zones for high availability.
This flexibility means startups can start small and grow without re-architecting their entire system.
2. Cost Efficiency Through Pay-as-You-Go Pricing
Traditional IT infrastructure requires large upfront investments. With AWS, you only pay for what you use—no capital expenditure needed.
- No long-term contracts or minimum fees.
- Reserved Instances offer up to 75% savings for predictable workloads.
- Spot Instances allow bidding on unused EC2 capacity at up to 90% off.
This pricing model democratizes access to enterprise-grade technology, especially for small businesses and startups.
3. Global Reach with Regional Data Centers
AWS operates in 33 geographic regions worldwide, with 105 Availability Zones—and expanding. This global footprint ensures low latency and compliance with local data regulations.
- Deploy applications closer to users for faster performance.
- Meet data sovereignty requirements by choosing region-specific deployments.
- Leverage AWS Edge Locations (over 400) via CloudFront for content delivery.
For companies aiming for international expansion, AWS provides a ready-made global infrastructure.
4. Robust Security and Compliance Framework
Security is not an afterthought in AWS—it’s built into every layer. AWS shares responsibility with customers, handling physical security while users manage access and data protection.
- AWS complies with standards like ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, HIPAA, GDPR, and FedRAMP.
- Tools like AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) control user permissions precisely.
- Encryption at rest and in transit is standard across most services.
Even highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare trust AWS with sensitive data.
5. Innovation at Speed with Cutting-Edge Services
AWS continuously introduces new services, often months ahead of competitors. This rapid innovation cycle empowers developers to build smarter, faster solutions.
- AI/ML services like SageMaker and Rekognition simplify machine learning integration.
- IoT Core enables secure communication between devices and the cloud.
- Quantum Computing via Braket opens doors to experimental computing.
With AWS, staying ahead of the tech curve isn’t just possible—it’s encouraged.
6. Disaster Recovery and High Availability
Downtime costs businesses millions. AWS provides tools to design resilient architectures that withstand failures.
- Multi-AZ deployments for RDS ensure database redundancy.
- Backup and Restore with AWS Backup centralizes data protection.
- Disaster recovery strategies range from pilot light to multi-site active/active setups.
By leveraging AWS, organizations can achieve 99.99%+ uptime with proper configuration.
7. Strong Ecosystem and Community Support
AWS boasts one of the largest developer communities and partner networks in the world. This ecosystem accelerates learning, troubleshooting, and deployment.
- The AWS Marketplace offers thousands of pre-built software solutions.
- AWS Partners (like Accenture, Deloitte) provide consulting and migration support.
- Active forums, documentation, and free training via AWS Educate and AWS Skill Builder.
Whether you’re stuck on a bug or planning a complex migration, help is always within reach.
Core AWS Services You Need to Know
To truly harness the power of AWS, it’s crucial to understand its foundational services. These are the building blocks used in nearly every AWS architecture.
Amazon EC2: The Heart of AWS Compute
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) provides scalable virtual servers in the cloud. It’s the most widely used compute service in AWS.
- Choose from over 500 instance types optimized for compute, memory, GPU, or storage.
- Launch instances in minutes with customizable operating systems and configurations.
- Integrate with Auto Scaling and Elastic Load Balancing for dynamic resource management.
EC2 is ideal for web servers, application backends, and batch processing tasks. Learn more at AWS EC2 Official Page.
Amazon S3: Scalable Object Storage
Simple Storage Service (S3) is AWS’s flagship storage solution, designed for durability, availability, and security.
- Stores data as objects within buckets—ideal for backups, media files, and logs.
- Offers 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability over a given year.
- Supports lifecycle policies to automatically move data to cheaper tiers like S3 Glacier.
S3 is the foundation for data lakes, static website hosting, and disaster recovery. Explore it at AWS S3 Documentation.
AWS Lambda: Serverless Computing Power
Lambda lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. You pay only for the compute time you consume.
- Supports Python, Node.js, Java, Go, and .NET.
- Triggers can come from S3 uploads, API Gateway requests, or scheduled events.
- Ideal for microservices, real-time file processing, and chatbots.
Lambda enables rapid development and reduces operational overhead significantly.
How AWS Compares to Other Cloud Providers
While AWS leads the market, it’s not alone. Competitors like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer compelling alternatives. Understanding the differences helps you make informed decisions.
Market Share and Maturity
AWS holds approximately 32% of the global cloud infrastructure market, according to Synergy Research Group—significantly ahead of Azure (~23%) and GCP (~11%).
- AWS has been in the market longer, giving it a maturity edge.
- More services available (over 200 vs. Azure’s ~150 and GCP’s ~100).
- Broader third-party integrations and tooling support.
This maturity translates into more stable APIs, better documentation, and proven reliability.
Hybrid and On-Premises Integration
Microsoft Azure excels here due to deep integration with Windows Server, Active Directory, and Microsoft 365. However, AWS isn’t far behind.
- AWS Outposts brings native AWS services into on-premises data centers.
- Azure Stack does the same but is limited to Microsoft-centric environments.
- For hybrid scenarios involving non-Microsoft tech, AWS offers more flexibility.
If your organization runs mostly Microsoft tools, Azure may feel more natural. Otherwise, AWS provides broader compatibility.
Pricing and Cost Management
Pricing varies significantly based on use case. While AWS offers granular control, Azure sometimes wins in Microsoft-heavy environments due to bundled licensing.
- AWS provides detailed cost allocation tags and budget alerts.
- Azure Reserved VM Instances can be more cost-effective when combined with Enterprise Agreements.
- GCP leads in sustained use discounts and custom machine types.
However, AWS’s Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) calculator and Cost Explorer make financial planning transparent and actionable.
Real-World Use Cases of AWS in Action
The true test of any technology is how it performs in real-world scenarios. AWS powers some of the most innovative and high-traffic platforms on the planet.
Netflix: Streaming at Global Scale
Netflix runs almost entirely on AWS, handling over 250 million subscribers and petabytes of data daily.
- Uses EC2 for transcoding video content.
- Leverages S3 for storing movie and show files.
- Employs CloudFront for fast, reliable content delivery worldwide.
Without AWS, Netflix would struggle to maintain its streaming quality and uptime during peak hours.
NASA JPL: Exploring Space with AWS
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory uses AWS to process images from Mars rovers and other deep-space missions.
- Processes massive datasets using Amazon EC2 and Elastic MapReduce.
- Stores mission-critical data in S3 with strict access controls.
- Uses AWS Ground Station to communicate directly with satellites.
AWS enables scientists to analyze data faster and share discoveries with the public in near real-time.
Siemens: Industrial IoT on AWS
Siemens uses AWS IoT Core to connect industrial machines and gather operational data.
- Monitors equipment health to predict maintenance needs.
- Processes sensor data using AWS Lambda and Kinesis.
- Visualizes insights with Amazon QuickSight.
This digital transformation reduces downtime and improves efficiency across manufacturing plants.
Getting Started with AWS: A Step-by-Step Guide
Ready to dive into AWS? Here’s a practical roadmap to get you started without feeling overwhelmed.
Step 1: Create an AWS Account
Visit aws.amazon.com and sign up for a free account. You’ll need a credit card, but many services are free for 12 months under the AWS Free Tier.
- Choose the “Basic” plan unless you need enterprise support.
- Verify your email and phone number.
- Set up Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for added security.
Step 2: Explore the AWS Management Console
The AWS Console is your central hub for managing services. It’s user-friendly but packed with features.
- Use the search bar to find services quickly.
- Switch between regions using the dropdown in the top-right corner.
- Bookmark frequently used services like EC2, S3, and IAM.
Spend time navigating the interface—it’s the gateway to everything AWS.
Step 3: Launch Your First EC2 Instance
Let’s deploy a simple web server to see AWS in action.
- Go to EC2 Dashboard > Launch Instance.
- Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI), like Amazon Linux 2023.
- Select an instance type (t2.micro is free tier eligible).
- Configure security groups to allow HTTP (port 80) and SSH (port 22).
- Review and launch, then download your key pair (.pem file).
Once running, connect via SSH and install a web server like Apache or Nginx.
Step 4: Store Files in Amazon S3
Now, let’s upload a file to S3.
- Navigate to S3 and click “Create bucket.”
- Name your bucket (must be globally unique).
- Upload a test file (e.g., index.html).
- Enable static website hosting in the bucket properties.
You now have a publicly accessible website hosted on AWS—no servers to manage!
Step 5: Monitor and Optimize Costs
Even with the Free Tier, it’s wise to monitor usage.
- Set up AWS Budgets to receive alerts when spending exceeds thresholds.
- Use Cost Explorer to visualize spending trends.
- Enable Trusted Advisor for cost optimization recommendations.
These tools prevent surprise bills and help you use AWS efficiently.
AWS Certifications: Boost Your Career in the Cloud
Earning an AWS certification is one of the best career moves in tech today. It validates your skills and opens doors to high-paying roles.
Why Get AWS Certified?
AWS certifications are globally recognized and highly valued by employers.
- Average salary for AWS-certified professionals exceeds $130,000 (source: Global Knowledge).
- Demonstrates hands-on expertise in cloud architecture, security, and operations.
- Required for many cloud engineering and DevOps positions.
Whether you’re starting out or advancing your career, certification pays off.
Popular AWS Certification Paths
AWS offers a structured path from foundational to expert levels.
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner: Entry-level, ideal for non-technical roles.
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate: Most popular; focuses on designing scalable systems.
- AWS Certified Developer – Associate: For coders building applications on AWS.
- AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate: For operations and DevOps teams.
- Professional and Specialty Certifications: For advanced roles in security, machine learning, and migration.
Start with Cloud Practitioner, then choose a specialty based on your goals.
How to Prepare for AWS Exams
Success requires a mix of study, practice, and real-world experience.
- Use official AWS Training & Certification resources.
- Practice with hands-on labs on Qwiklabs or A Cloud Guru.
- Take mock exams to identify weak areas.
- Join study groups or Reddit communities like r/AWSCertifications.
Most exams cost $100–$300, so preparation is key to passing on the first try.
Future Trends Shaping AWS and the Cloud
The cloud isn’t standing still. AWS continues to evolve, driven by emerging technologies and shifting business needs.
Rise of Serverless and Event-Driven Architectures
Serverless computing, led by AWS Lambda, is becoming the default for new applications.
- Reduces operational complexity and cost.
- Scales automatically to zero when idle.
- Encourages modular, microservices-based design.
Expect more services to adopt serverless models, reducing the need for traditional servers.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
AWS is embedding AI into its core services, making advanced capabilities accessible to all.
- Amazon Bedrock offers foundation models for generative AI.
- SageMaker Autopilot automates model training and deployment.
- Rekognition, Transcribe, and Polly add AI-powered features to apps.
Soon, every developer will be able to build AI-enhanced applications without deep ML expertise.
Sustainability and Green Cloud Computing
AWS is committed to running on 100% renewable energy by 2025 (already at 90% as of 2023).
- Energy-efficient data centers reduce carbon footprint.
- Customers can track their environmental impact via AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool.
- Optimized hardware (like Graviton chips) uses less power than traditional processors.
Sustainability is no longer optional—AWS is leading the charge in green cloud innovation.
What is AWS used for?
AWS is used for a wide range of applications, including hosting websites and web apps, storing and analyzing big data, running machine learning models, powering IoT devices, and supporting enterprise IT infrastructure. It’s used by startups, governments, and global enterprises alike.
Is AWS free to use?
AWS offers a Free Tier that includes limited access to many services for 12 months, plus some services that are always free. However, most production workloads incur costs based on usage. It’s important to monitor your usage to avoid unexpected charges.
How does AWS pricing work?
AWS uses a pay-as-you-go model. You pay only for the services you use, with no upfront costs or long-term commitments. Pricing varies by service and can include factors like compute time, storage volume, data transfer, and request count. Tools like the AWS Pricing Calculator help estimate costs.
What is the difference between AWS and Azure?
AWS has a larger market share, more services, and greater global reach. Azure integrates better with Microsoft products and is often preferred by enterprises already using Windows Server and Office 365. The choice depends on specific needs, existing infrastructure, and technical requirements.
How do I learn AWS?
You can learn AWS through free resources like AWS Skill Builder, paid courses on platforms like Udemy or Coursera, hands-on practice in the AWS Console, and by pursuing AWS certifications. Starting with the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner exam is a great way to build foundational knowledge.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is more than just a cloud provider—it’s a catalyst for digital transformation. From its pioneering role in creating the cloud economy to its ongoing leadership in innovation, AWS empowers businesses to scale, secure, and innovate like never before. Whether you’re launching your first app or managing a global enterprise infrastructure, AWS offers the tools, reliability, and support you need. The future of technology runs on the cloud, and AWS is at the heart of it. Now is the time to dive in, learn, and leverage the full power of AWS to achieve your goals.
Further Reading: